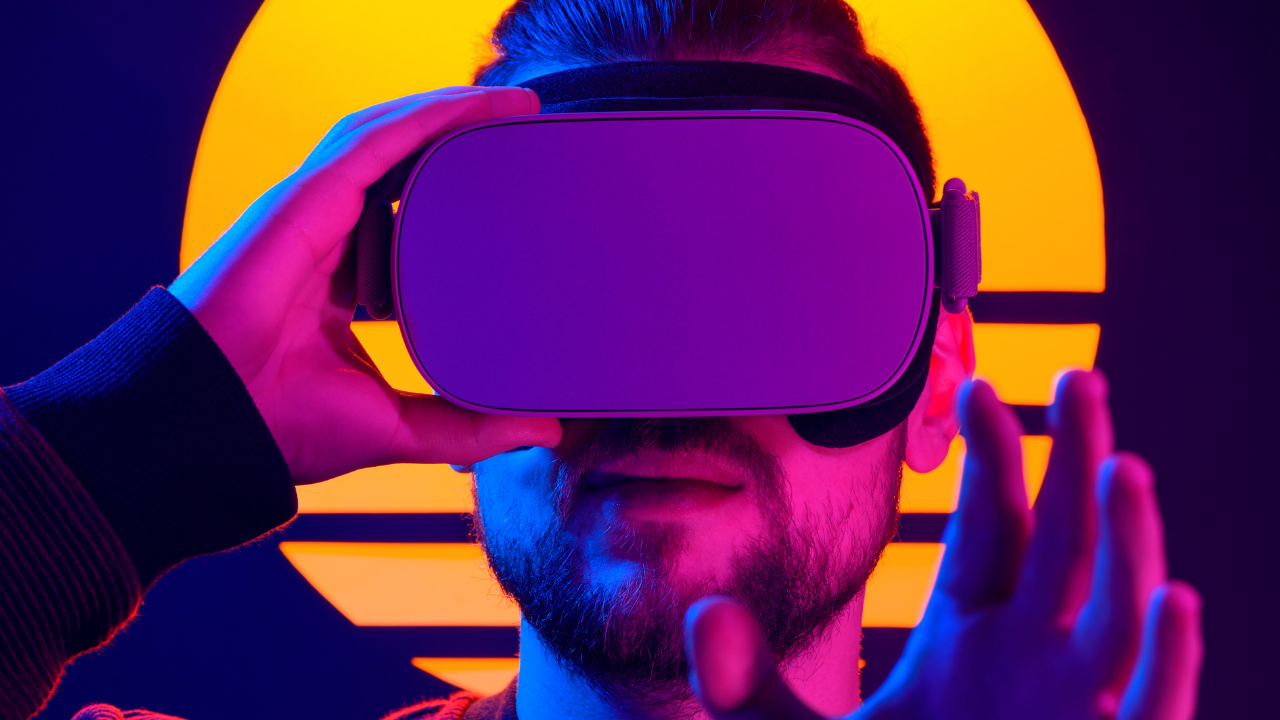
- Imagine putting on a VR headset and “attending” a business meeting anywhere in the world.
- The metaverse – an artificial universe blending AR and VR technology – makes this possible.
- To understand how it works, here are 10 things you need to know about the metaverse and how it relates to the future of work.
The pandemic has completely transformed the global workforce including how we work, where we work, and the tools we use to be productive.
Among the technological trends that have emerged in popularity during this time has been the metaverse, which is a digital universe that melds virtual and augmented reality to build an immersive experience.
This technology has previously been used for video game platforms.
Now, companies like Meta (formerly known as Facebook) have tried their hand at colonizing the virtual universe.
It’s not surprising that the idea of the metaverse is generating such a massive buzz, but many people may still be confused about the concept of it.
Here are ten things you need to know about the metaverse:
1. The metaverse is an artificial universe made possible by AR and VR technology
While wearing a VR headset, you would be able to “attend” a business event or even a virtual concert – as if you were there in person.
The metaverse creates a three-dimensional experience so people can interact with one another in a more immersive way, but not physically.
It fuses the real and virtual worlds, giving users a 3D space to meet, work, shop, and do everything that you can on the internet and more.
As Mark Zuckerberg likes to call it: an embodied internet.
2. Anyone is able to join the metaverse
The metaverse is a virtual and interoperable world. Interoperability is a core component of the metaverse, which means that information is exchanged between different systems seamlessly. Entering the metaverse is easier than you might think.
If you have access to a VR headset, you have access to the metaverse – although a VR headset will set you back about $300.
Just as anyone may have access to the internet, the metaverse is also as easily accessible. You will need to download the right applications in order to access the metaverse though, such as the game The Sandbox – one of the most popular decentralized metaverse games. It allows users to create, build, and monetize from the virtual worlds they’re creating within the digital world.
3. The metaverse can be used to work, game, and travel
A lot is possible in the metaverse (all virtually of course).
Supporters of the metaverse envision its users working, playing, gaming and staying connected with friends through everything from concerts, conferences, and virtual trips around the world.
4. Things in the metaverse will cost as well as generate money
Metaverse participants are able to engage in decentralized virtual economies powered by cryptocurrency (like Sensorium Galaxy’s very own SENSO).
This includes marketplaces where users can buy, sell and exchange items such as digital assets like avatars, virtual clothing, NFTs and event tickets.
The metaverse equals big money. By some estimates, the annual revenue opportunity for virtual worlds could be worth as much as $1 trillion, across segments like advertising, digital events and e-commerce.
5. You can own and sell land in the metaverse
Many people are considering purchasing digital property as an asset that will appreciate.
Metaverse coins have amassed large growth. As a result, owning property within metaverse games could be lucrative for the potential return on investment.
Popular lands on the metaverse available for sale are The Sandbox, Decentraland, and Cryptovoxels, which are all available on OpenSea.
Decentraland broke yet another metaverse record after a virtual estate sold for $2.4 million.
6. The metaverse isn’t owned by anyone
The metaverse isn’t owned by a corporation or a single platform, but by all of its users, who can also take control over their private data.
The W3C (World Wide Web Consortium) decides the standards for the metaverse, which is led by the creator of the world wide web – a man who has never sought to overly monetize his creation: Tim Berners-Lee.
However, the metaverse doesn’t have any apparent creator.
7. The metaverse might be safer than you think
Money-wise, the metaverse is secure because blockchain technology ensures that all transactions within a virtual world are public, easily tracked and safe at all times.
As for cybersecurity, the metaverse will increase the number of places that can be attacked. Although the underlying systems will remain the targets for stealing data, this could change as the platforms become more popular.
As for identity theft, when avatars are used as a form of identification, the person and personal data become susceptible to being copied, stolen, erased or manipulated. But biometric identification could be a solution in the future.
8. The way we work will most likely be impacted by the metaverse
Working online is already a reality for many of us. The metaverse would be just a continuation of that as Facebook has already released Horizon Workrooms.
Other tech giants like Microsoft are following suit and we can only expect more companies to try and send their workers into the metaverse.
In less than ten years, VR will be used in 23 million jobs worldwide – thus, humanity’s entrance into the metaverse.
Metaverse-style ideas might help people organize the way we work – and more broadly – society, in a more productive manner.
Shared standards and protocols that bring disparate virtual worlds and augmented realities into a single, open metaverse could help people work together and cut down on duplication of effort.
9. Blockchain technology is central to the development of the metaverse
Metaverse blockchain technology is still under development, but the concept of this digital world is well-developed.
Blockchain has proven to be a useful technology for six key metaverse areas: digital proof of ownership, digital collectibility, transfer of value, governance, accessibility, and interoperability.
But what exactly is a blockchain?
It’s shared, unchangeable, and facilitates the process of recording transactions and tracking assets in a business network.
An asset can be tangible (a house, car, cash, land) or intangible (intellectual property, patents, copyrights, branding).
Virtually anything of value can be tracked and traded on a blockchain network, reducing risk and cutting costs for all involved.
Blockchain technology provides a transparent and cost-effective solution, making it an ideal fit for the metaverse.
10. The metaverse isn’t here just yet
A fully-fledged metaverse might be years, if not at least a whole decade away.
There are still plenty of technical hurdles to overcome, starting with the fact that the world doesn’t have an online infrastructure that could sustain millions (or even billions) of people using the metaverse at the same time.
Uninterrupted and reliable internet connection is a key building block of the metaverse, because a glitchy virtual world scenario is not exactly what the metaverse is supposed to look like.
Technology like 5G and edge computing is still under development, and currently unable to meet the demands of a complex infrastructure like a metaverse.