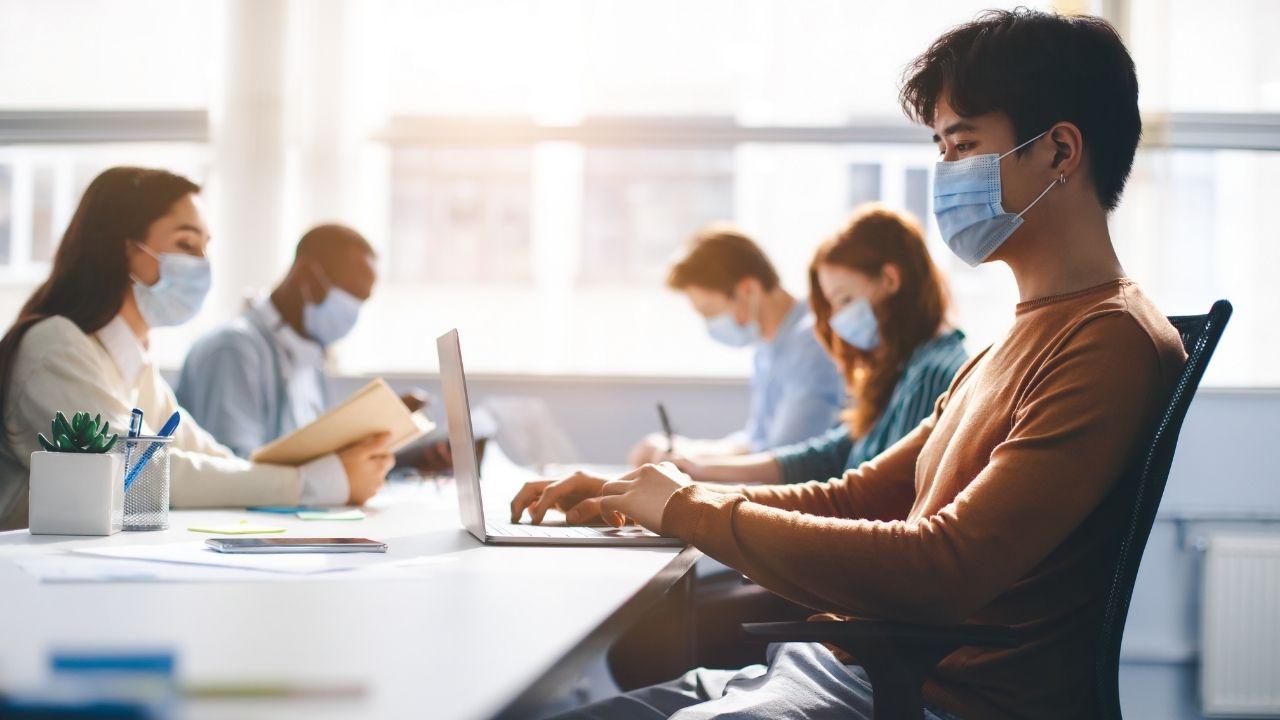
Following the decline of Covid-19 cases from the historic high driven by the Omicron variant, major cities are beginning to drop their pandemic-related restrictions.
For instance, Washington D.C. just announced that “indoor venues will no longer be required to verify that patrons are vaccinated,” although individual businesses can create their own policies and mandates.
Philadelphia also revealed that vaccine mandates would be adjusted depending on Covid-19 metrics, but that proof of vaccination would no longer be required for indoor dining.
Seattle also revealed that it was dropping vaccine mandates for indoor activities starting March 1.
Although many cities are beginning to move forward with a post-pandemic society, some city workers are facing repercussions for refusing vaccinations. For instance, New York City Mayor Eric Adam revealed that less than 1% of city employees were fired for not complying with the city’s vaccine mandate.
Despite the U.S. Supreme Court striking down the Biden administration’s vaccine mandate for large companies, some states and cities have implemented their own version of the executive order.
For example, states like California and New Jersey require vaccinations for healthcare professionals, government employees, and education workers.
Alongside states setting their own rules, many companies have revealed their own vaccination requirements for employees, including:
- Apple
- AT&T
- DoorDash
- Ford
- General Electric
- IBM
- Lyft
- McDonald’s
The Pentagon also announced that all active-duty service members would need to be fully vaccinated against Covid-19 and revealed that 96% had been vaccinated as of January.
Organizations, governments, and companies are all seeking to move past the pandemic and instead learn to operate alongside it.
One of the main strategies these entities are taking is requiring vaccines as they have been found to greatly decrease the risk of contracting Covid-19 or experiencing a severe case of the virus.